- 1 1. Introduction: Why the term "lszh compound hs code" is a focus in the industry
- 2 2. What is the low smoke zero halogen compound (LSZH compound)?
- 3 3. HS code basics: Understanding customs classification and rules
- 4 4. 2025 LSZH compound's most common HS codes explained
- 5 5. Regional practices: differences when using "hs code for lszh insulation compound"
- 6 6. Enterprise‑perspective: The case of Hangzhou Meilin New Material Technology Co., Ltd.
- 7 7. Practical recommendations: key points for exporters or buyers handling HS code for LSZH compounds
- 8 8. Conclusion: Trends and outlook for LSZH compound HS coding
- 9 FAQ
In the rapidly evolving wire and cable materials industry, the designation and compliance of the LSZH compound HS code have become critical for manufacturers, exporters and importers alike. This article offers a professional, detailed, and up‑to‑date guide to the latest HS code practices for low smoke zero halogen (LSZH) compounds in 2025, combining global trade data, regional regulatory nuances, and practical enterprise insights.
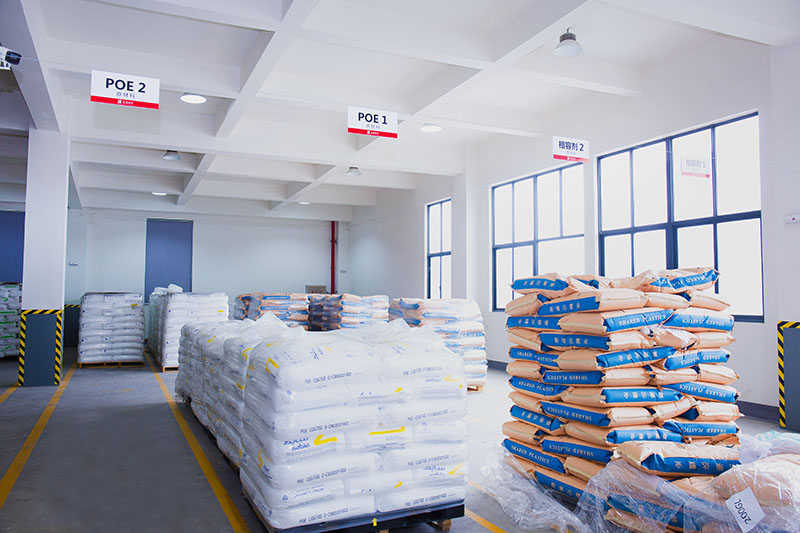
ML-TH9002D Thermoplastic LSZH flame- retardant Dca grade sheath material
1. Introduction: Why the term "lszh compound hs code" is a focus in the industry
As fire safety regulations tighten and international trade expands, the correct classification of LSZH compounds via HS codes directly affects customs clearance, duty calculations and market access. Many stakeholders now search for "lszh compound hs code 39013000" or "low smoke zero halogen compound hs code 39019000" to ensure compliance and reduce logistical risk.
2. What is the low smoke zero halogen compound (LSZH compound)?
2.1 Definition & key characteristics
- LSZH stands for Low Smoke Zero Halogen — materials that, when exposed to fire, emit limited smoke and no halogen‑based acid gases.
- A typical LSZH compound uses thermoplastic or thermoset matrices combined with inorganic fillers (e.g., aluminium trihydrate) to suppress flame, smoke and toxic gas release.
- Its applications include insulation and jacketing for cables in enclosed or poorly‑ventilated environments (e.g., railway tunnels, shipboard, buildings).
2.2 Application areas overview
- Cable jackets for data centres, public buildings, transportation systems.
- Wire harnesses in rail, shipbuilding, underground facilities.
- Specialized cable compounds where fire safety and low‑toxic emission are vital.
3. HS code basics: Understanding customs classification and rules
3.1 Structure and logic of HS codes
The Harmonized System (HS) code is a globally‑recognized customs nomenclature used to classify traded goods. Each code reflects the product's material, form, function and sometimes origin. Choosing the correct code impacts duty rate, licensing and trade compliance.
3.2 Relation to "lszh cable compound hs code classification"
- Compounds used as insulation or jacketing for cables may fall under different headings depending on their composition and intended use.
- Mis‑classification can lead to delays, penalties or mis‑application of duty rates.
4. 2025 LSZH compound's most common HS codes explained
4.1 Code 3901 series (e.g., 39013000) applicability
The heading 3901 covers "Polymers of ethylene, in primary forms". Some LSZH compounds that are ethylene‑based thermoplastic granules are classified here. Trade data shows LSZH compound under HS 39013000.
4.2 Code 39019 series (e.g., 39019000) applicability
The heading 39019000 corresponds to "Polymers of other olefins, in primary forms"; some LSZH compounds are captured here depending on their polymer matrix. Trade data confirms LSZH under 39019000.
4.3 Comparison table: major differences between the codes
| HS Code | Description | Typical LSZH Use‑Case | Notes |
| 39013000 | Polymers of ethylene, primary forms | Ethylene‑based LSZH granules for jacketing/insulation | Well‑used in EU/India import‑data. |
| 39019000 | Polymers of other olefins, primary forms | LSZH compounds with alternative olefin base | Trade data shows shipments under this code. |
5. Regional practices: differences when using "hs code for lszh insulation compound"
5.1 China customs practice analysis
- Chinese export data show LSZH compounds classified under various 39‑series headings (e.g., 3901200091) when used for cable heathing.
- Domestic exporters must review both polymer base and end‑use (insulation vs jacketing) to choose the proper sub‑heading.
5.2 European import scenarios & data
- Europe exports LSZH compound under HS 39013000.
- Importers often request detailed technical specification to support correct HS code declaration.
5.3 India and emerging markets trends
- India's import database shows large volumes of LSZH compound under 39013000 and 39019000.
- Growing markets require vigilant compliance with HS code classification to avoid regulatory issues.
6. Enterprise‑perspective: The case of Hangzhou Meilin New Material Technology Co., Ltd.
6.1 Company overview & production capacity
Founded in July 1994 (formerly Zhejiang Linan Hongyan Plastic Factory) and with the establishment of Hangzhou Meilin Special Material Co., Ltd in August 2024, the two companies – together – operate three production plants located at:
- No. 619, Linglongshan Road, Linglong Industrial Park, Lin'an District, Hangzhou City, Zhejiang Province, China.
- No. 259, Xingyu Street, Linglong Sub‑district, Lin'an District, Hangzhou City, Zhejiang Province, China.
- No. 6, Guifangqiao, Guifangqiao Industrial Zone, Tianmushan Town, Lin'an District, Hangzhou City, Zhejiang Province, China.
The group has a registered capital of RMB 85 million, covers an area over 40,000 m², with construction area over 45,000 m², and has completed 31 advanced automated production lines. With more than 210 employees (including 5 senior engineers and over 30 science & technology staff) the company is a leading professional manufacturer of cable materials in the region. In 2024 the output value exceeded RMB 700 million. Products include LSZH, PVC, FR‑PE, PE, XLPE, SEMICON and SOLAR CABLE.
6.2 HS code compliance & international trade practice
- The company has deep experience in assigning the correct HS code for its LSZH compounds, ensuring export shipments are classified under the appropriate heading (such as 39013000 or 39019000) based on compound chemistry and application.
- By working across domestic and overseas markets, the company understands the nuances of global "lszh jacketing compound hs code global" classification and helps customers avoid mis‑declaration risks.
7. Practical recommendations: key points for exporters or buyers handling HS code for LSZH compounds
7.1 Risks of incorrect code selection
- Using the wrong HS code can result in customs delays, extra duties or non‑compliance penalties.
- Mis‑classification may lead to mismatched trade statistics and hinder market analytics.
7.2 Compliance best practices & process optimization
- Compile full technical documentation: polymer base, filler content, end‑use (insulation vs jacketing), colour & form.
- Consult with customs broker or classification specialist early to map to correct heading (e.g., 39013000 vs 39019000 vs other 39‑series).
- Keep audit‑trail of past shipments and classification decisions to support customs queries.
- Monitor regional changes: different countries may interpret compound classification differently depending on local rules.
8. Conclusion: Trends and outlook for LSZH compound HS coding
As fire‑safety regulations and environmental standards tighten globally, and as the demand for low‑smoke, halogen‑free cable compounds rises, correct HS classification of LSZH compounds becomes ever more critical. In 2025, exporters and purchasers must stay abreast of distinguishing between codes like 39013000 and 39019000, understand regional nuances, and partner with experienced manufacturers like our company who already have robust HS code compliance practices. By doing so, stakeholders will be well‑positioned to leverage the growth of the LSZH market while avoiding classification and trade risks.
FAQ
- Q1: What is the most common HS code for LSZH compounds globally?
- A1: Many shipments show use of code 39013000 and 39019000, though the correct code depends on polymer type and application.
- Q2: How do I determine whether to use code 39013000 or 39019000 for an LSZH compound?
- A2: The key is to identify the polymer base (ethylene vs other olefins) and intended use (insulation, jacketing). Consult classification guides and customs counsel.
- Q3: Are there regional differences in how LSZH compounds are coded?
- A3: Yes. For example, in China some compounds are listed under 3901200091 for LSZH sheath compounds. In India and Europe, 39013000 or 39019000 are frequent.
- Q4: What happens if the HS code for an LSZH compound is declared incorrectly?
- A4: Possible consequences include customs delays, increased duties, fines or shipment rejection. Precise classification is essential.
- Q5: How can a manufacturer like ours support customers in HS code classification for LSZH compounds?
- A5: By providing full technical datasheets (polymer matrix, filler content, end‑use), advising on likely applicable HS codes, and sharing previous export classification precedents as part of documentation.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский