- 1 Introduction
- 2 What Are LSZH Compounds?
- 3 Key Applications in Transportation Sector
- 3.1 Rail transit & underground systems – "low smoke zero halogen cable material for rail transit"
- 3.2 Tunnel, subway and mass transit systems – "zero halogen flame retardant cable compound for mass transit systems"
- 3.3 Automotive wiring harnesses & special vehicles – "LSZH compound selection criteria for automotive wiring harnesses"
- 4 How to Choose the Right LSZH Compound for Transportation Cables
- 5 Case Study – Our Company's Production Capabilities & Advantage
- 6 Challenges and Future Trends for LSZH Compounds in Transportation
- 7 FAQ
- 7.0.1 1. What does LSZH mean and why is it important for transportation cables?
- 7.0.2 2. How is a "halogen‑free flame retardant compound for underground transport cables" different from standard PVC compounds?
- 7.0.3 3. What criteria should be considered when selecting an LSZH compound for automotive wiring harnesses?
- 7.0.4 4. Are there trade‑offs when using a "polyolefin LSZH sheath compound for tunnel cable applications" instead of conventional material?
- 7.0.5 5. What future trends should manufacturers expect in "zero halogen flame retardant cable compound for mass transit systems"?
- 8 Conclusion
In today's high‑demand transit infrastructure and mass‑mobility systems, cable safety is a non‑negotiable concern. This article explores how LSZH Compounds For Transportation Cables provide superior performance, how to select the right formulation, and how our company, Hangzhou Meilin New Material Technology Co., Ltd. and Hangzhou Meilin Special Material Co., Ltd., is positioned to meet this demand.
Introduction
Why transportation‑cable environments demand specialized compounds
- Enclosed or poorly ventilated spaces such as tunnels, underground transit, railway carriages, and mass transit stations face high fire‑risk scenarios.
- In such scenarios, dense smoke or corrosive gases from burning cables can severely hamper evacuation and damage equipment.
- Hence the rise of safer alternatives like low smoke zero halogen cable material for rail transit.
Overview of our company
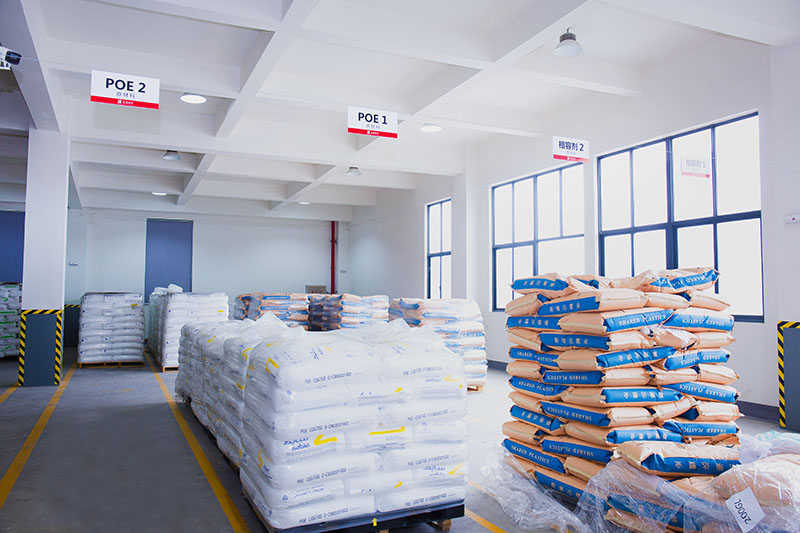
Founded in July 1994 (formerly Zhejiang Linan Hongyan Plastic Factory), Hangzhou Meilin New Material Technology Co., Ltd., along with Hangzhou Meilin Special Material Co., Ltd. (established August 2024), operates three production plants located at No. 619 Linglongshan Road & No. 259 Xingyu Street & No. 6 Guifangqiao, Lin'an District, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China. With a total registered capital of RMB 85 million, covering more than 40,000 m² site area and 45,000 m² built area, the company houses 31 advanced automated production lines. With over 210 employees, including 5 senior engineers and more than 30 science & technology management personnel (accounting for >30% of workforce), the company achieved output value exceeding RMB 700 million in 2024. Our product range includes LSZH, PVC, FR‑PE, PE, XLPE, SEMICON and SOLAR CABLE, serving domestic and overseas markets.
ML-FJ125QA 125℃ irradiated halogen- free flame-retardant insulation material for incar cables
What Are LSZH Compounds?
Definition and material composition
The term LSZH Compounds For Transportation Cables refers to specialised jacketing or insulation compounds that are low smoke (i.e., minimal smoke when burnt) and zero halogen (i.e., no halogen elements like chlorine, bromine) in their formulation.
Typically based on halogen‑free polyolefins (e.g., EVA, PE) filled with metal hydroxides (e.g., aluminium hydroxide) the compounds suppress flame, reduce smoke and avoid halogen‑acid gas release.
Core benefits of LSZH in cable systems
Low smoke emission
- Significantly lower optical smoke density in a fire, improving visibility for evacuation.
- Less smoke means reduced damage to surrounding equipment due to soot accumulation.
Zero halogen gas release
- No halogen‑acid gases (such as HCl) produced during combustion, preventing corrosive gas damage and toxic exposure.
- Better protection of electronics and human health in confined spaces.
Enhanced fire safety in confined spaces
- Ideal for environments with limited ventilation like tunnels, rail systems, underground transport hubs.
- Aligns with increasing regulatory demands for safe cable materials in transit and aviation sectors.
Key Applications in Transportation Sector
Rail transit & underground systems – "low smoke zero halogen cable material for rail transit"
In rail systems, especially underground or enclosed carriages, installing cables with minimal smoke and zero halogen emissions is critical. For example, visibility loss and toxic gas accumulation are major hazards in tunnels.
Tunnel, subway and mass transit systems – "zero halogen flame retardant cable compound for mass transit systems"
Mass transit systems (metros, airports, transit hubs) require reliable cable materials that will not compromise occupant safety or equipment integrity — making LSZH compounds an increasingly standard choice.
Automotive wiring harnesses & special vehicles – "LSZH compound selection criteria for automotive wiring harnesses"
In modern vehicles (especially EVs and autonomous vehicles) the wiring harness is densely packed and sometimes located in enclosed compartments. Selecting an LSZH jacketing compound helps reduce risk of smoke/toxic gas release during fire scenarios.
How to Choose the Right LSZH Compound for Transportation Cables
Matching compound to environment and use case
Underground vs open‑air installations
- Underground and tunnel installations have strict requirements for low smoke and halogen‑free performance.
- In open‑air installations risk is lower, so cost‑benefit analysis becomes important.
High‑temperature and chemical exposure zones
- Automotive under‑hood, engine compartments, or external vehicle wiring may require LSZH compounds that withstand oil, heat, vibration.
- Sheath formulations for tunnel cables may demand abrasion, UV and ageing resistance in addition to fire safety.
Comparing traditional materials vs LSZH
When comparing materials, note: traditional PVC or FR‑PVC compounds may offer good general performance, but when it comes to fire safety in enclosed transport environments, an LSZH formulation often offers major advantages. Below is a comparison:
| Property | LSZH Compound | Traditional PVC/FR‑PVC |
| Smoke density | Very low | Very high |
| Toxic/corrosive gas release | Minimal/none | High (e.g., HCl) |
| Flame retardancy in enclosed spaces | Excellent for confined spaces | Good, but with more risk of secondary damage |
| Mechanical/flexibility trade‑off | Improved, but sometimes higher cost or filler content [oaicite:16] | Well established, lower cost |
Typical standards and testing to verify suitability
- Smoke emission test (e.g., IEC 61034) and acid gas test (IEC 60754) for LSZH performance.
- Flame propagation tests for cable sheaths in transit environments (e.g., EN 45545 for rail).
- Ensure compound manufacturer provides detailed data sheets and relevant certification.
Case Study – Our Company's Production Capabilities & Advantage
Company history & manufacturing footprint
As introduced, Hangzhou Meilin New Material Technology Co., Ltd. and Hangzhou Meilin Special Material Co., Ltd. combine experience since 1994 with modern production bases (three plants) and 31 advanced automated lines. This manufacturing strength enables consistent, high‑quality output of LSZH compounds tailored for transportation cable applications.
Production lines, certifications, output value
With registered capital RMB 85 million, covering >40,000 m² area and output value above RMB 700 million in 2024, the companies are well positioned to serve large‑scale cable projects with demanding safety and environmental requirements.
Product portfolio and what sets our LSZH compounds apart
- We provide LSZH compounds alongside PVC, FR‑PE, PE, XLPE, SEMICON and SOLAR CABLE materials — meaning integrated support for cable manufacturers.
- Our LSZH formulations emphasise both flame‑safety and mechanical/processability — aligning with "polyolefin LSZH sheath compound for tunnel cable applications".
- We target not only domestic but international markets, supporting export requirements and global safety standards.
Challenges and Future Trends for LSZH Compounds in Transportation
Common technical trade‑offs
- Earlier generations of LSZH compounds may have had reduced flexibility or higher cost compared to PVC.
- High filler content (to achieve low smoke/zero halogen) may impact mechanical or chemical resistance — need for formula optimisation.
Emerging requirements in rail, automotive, tunnel sectors
- Greater expectation for multifunctional materials: e.g., higher temperature rating, tamper‑resistance, chemical resistance.
- In automotive EV wiring harnesses: expectation of LSZH use in confined vehicle spaces for fire‑safety. ("halogen‑free flame retardant compound for underground transport cables" and automotive variants)
- Increasing regulatory pressure for sustainable, recyclable materials and lower environmental footprint.
What to look for next in LSZH development
- Improved processability (e.g., lower extrusion die build‑up, better colour stability) while maintaining flame/smoke performance.
- Cross‑linked LSZH grades for very high‑temperature or oil/chemical exposed environments.
- Bio‑based or recyclable LSZH materials to support green infrastructure and sustainability goals.

FAQ
1. What does LSZH mean and why is it important for transportation cables?
"LSZH" stands for "Low Smoke Zero Halogen". In transportation cable environments, using LSZH compounds ensures minimal smoke generation and no halogen‑acid gas release during a fire, which significantly improves safety for both people and equipment.
2. How is a "halogen‑free flame retardant compound for underground transport cables" different from standard PVC compounds?
Standard PVC compounds can emit dense black smoke and corrosive gases (e.g., HCl) when burning. In contrast, a halogen‑free flame retardant compound (i.e., LSZH) produces very low smoke and essentially no halogen‑acid gases, reducing fire risk and equipment damage.
3. What criteria should be considered when selecting an LSZH compound for automotive wiring harnesses?
Key criteria include: temperature range, chemical/oil resistance, mechanical flexibility, smoke density, halogen‑free gas release, processability and cost. In other words, for automotive use you must focus on "LSZH compound selection criteria for automotive wiring harnesses".
4. Are there trade‑offs when using a "polyolefin LSZH sheath compound for tunnel cable applications" instead of conventional material?
Yes, while the polyolefin LSZH sheath compound offers superior fire/smoke/halogen performance, there may be higher cost, more fillers (impacting flexibility), or additional processing considerations. The key is balancing fire safety with mechanical/process requirements.
5. What future trends should manufacturers expect in "zero halogen flame retardant cable compound for mass transit systems"?
Expect demands for improved sustainability (recyclable, bio‑based materials), higher temperature rating, more chemical resistance, better processability, and stricter regulations in mass transit systems that will drive innovation in zero halogen flame retardant cable compounds.
Conclusion
In summary, for the transportation sector — whether in rail transit, tunnel systems, mass transit hubs or automotive wiring — choosing the right LSZH Compounds For Transportation Cables can significantly improve safety, reduce risk and comply with evolving regulation. With a trusted partner such as Hangzhou Meilin New Material Technology Co., Ltd. and Hangzhou Meilin Special Material Co., Ltd., manufacturers can work with a strong compound supplier that combines deep experience, broad product portfolio and modern production capability.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский