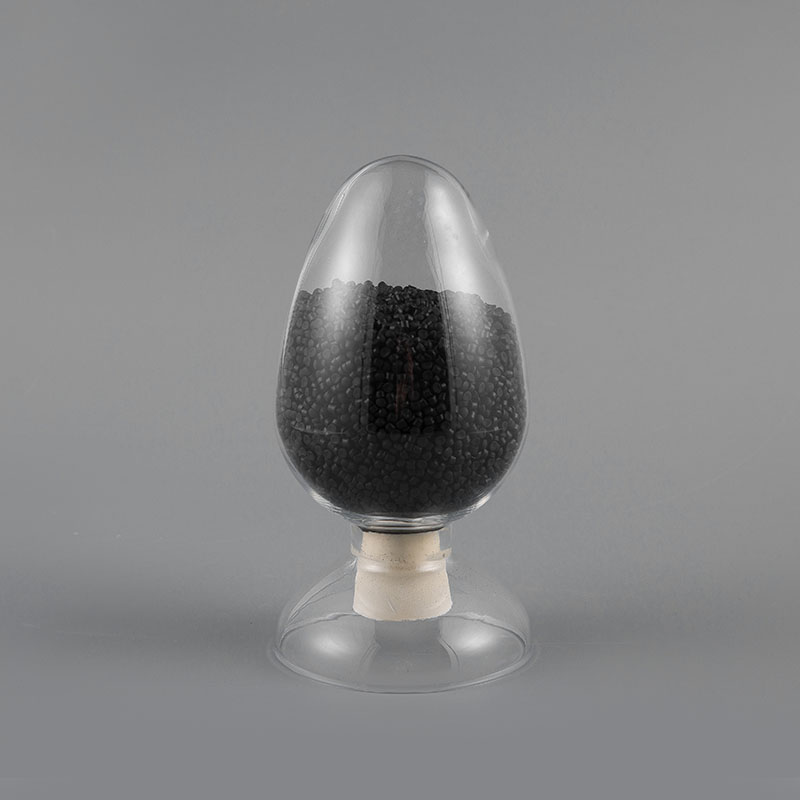
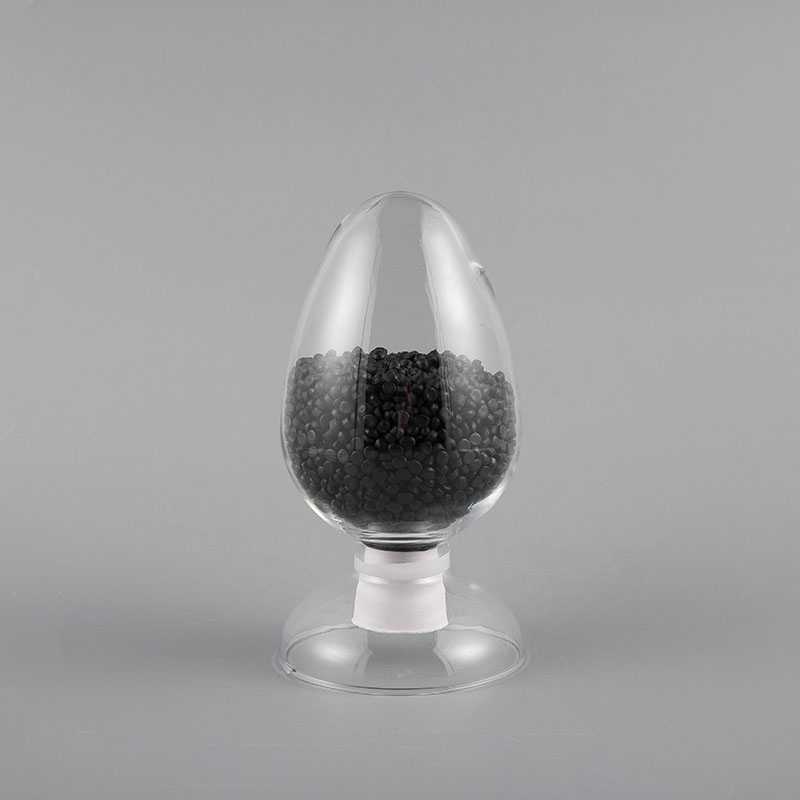
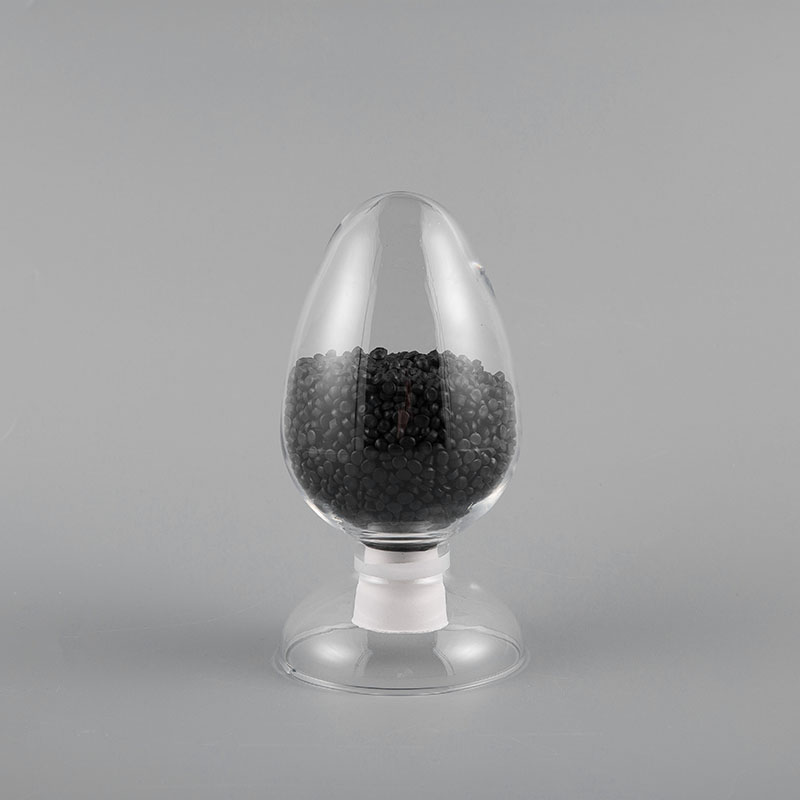
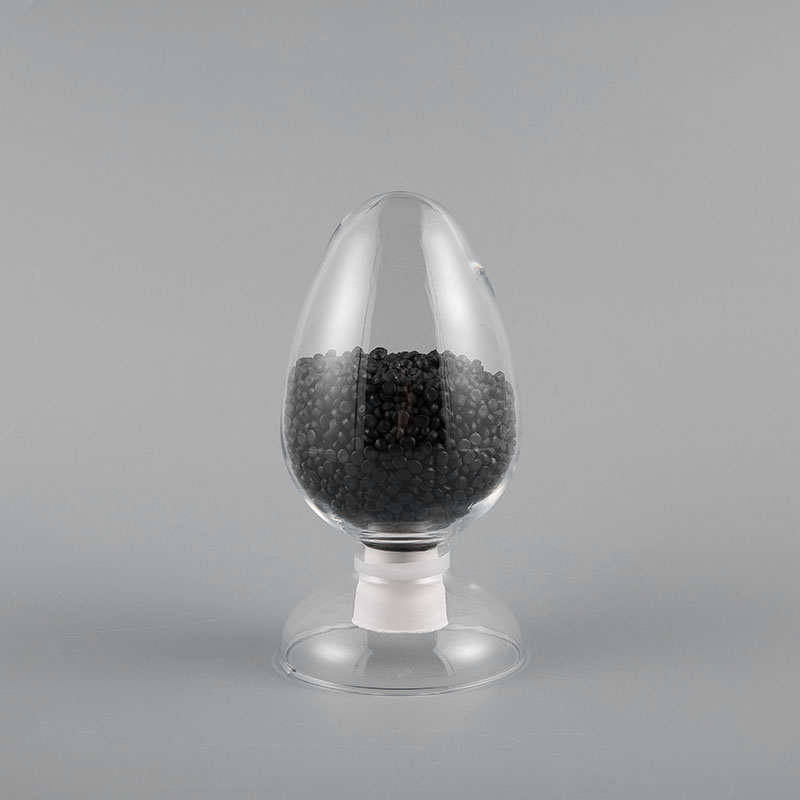
HⅡ-90 ST6 Type 90℃ Soft Polyvinyl Chloride Sheath Compound for Electric Floor Heating is specially d...
ABOUT US
30YEARS OF
EXPERIENCE
About Us
Coming From China, Marketing To The World.
Hangzhou Meilin New Material Technology Co., Ltd. is China ODM/OEM Heating Cable Compound Suppliers and Wholesale Heating Cable Compound, we were established in July 1994 (formerly known as Zhejiang Lin'an Hongyan Plastic Factory). The company has two factories located at 619 Linglongshan Road and 259 Xingyu Street, Lingqiu Street, Linglong Industrial Park, Lin'an District, Hangzhou City. The registered capital of the company is 75 million yuan, covering an area of over 18000 square meters and a building area of over 30000 square meters. Currently, modern industrial factories and 18 advanced automated production lines have been built. The new factory area will be produced in 2021, making it the cleanest and most beautiful professional cable material manufacturer in the entire region—agreement conditions.
-
admin 12 Feb 2026
Why Are LSZH Compounds for Communication Cables Essentia...
Read MoreAs global data consumption surges, the architectural density of data centers and the complexity of public infrastructure have reached unprecedented levels. In these confined, high-value environments, ...
-
admin 04 Feb 2026
Meeting Global Compliance: Critical Requirements for PVC...
Read MoreThe global cable manufacturing landscape is undergoing a rigorous transition driven by stringent safety and environmental regulations. For industry professionals, understanding the technical nuances o...
-
admin 29 Jan 2026
Why Should You Switch to LSZH Compounds For Communicatio...
Read MoreIn the engineering of modern public infrastructure—such as subway systems, airports, and high-rise data centers—the selection of cabling materials is a critical safety decision. The transition from tr...
-
admin 22 Jan 2026
Navigating High-Speed Extrusion Challenges for LSZH Comp...
Read MoreAs global telecommunications infrastructure shifts toward 5G and high-density data centers, the demand for LSZH Compounds For Communication Cables has reached unprecedented levels. Unlike traditional ...
Heating Cable Compound Industry Knowledge
Explosion-Proof Heating Cables: Advanced Polymer Compounds for Hazardous Industrial Environments
In industries such as oil & gas, chemical processing, and mining, maintaining safe and efficient operations in hazardous environments requires specialized heating solutions. Explosion-proof heating cables, engineered with advanced polymer compounds, play a critical role in preventing equipment freeze-ups, maintaining viscosity in pipelines, and ensuring process stability—all while meeting stringent ATEX and IECEx certifications for explosive atmospheres.
Key Innovations in Heating Cable Compounds for Hazardous Zones
1. Self-Regulating PTC Heating Cable Materials
Modern explosion-proof heating cables often utilize positive temperature coefficient (PTC) materials, which automatically adjust heat output based on ambient conditions. Unlike traditional constant wattage heating cables, PTC polymer-based heating elements reduce overheating risks—a crucial feature in Class I, Division 1 (flammable gases) and Class II, Division 2 (combustible dust) environments.
Performance Comparison:
| Feature | Traditional MI Heating Cable | PTC Polymer-Based Heating Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Self-Regulation | No | Yes |
| Energy Efficiency | Low (fixed wattage) | High (adaptive output) |
| Explosion-Proof Certification | Requires additional shielding | Intrinsically safe design |
| Lifespan | 10-15 years | 15-20+ years |
| Installation Flexibility | Rigid, requires conduit | Flexible, easier routing |
| Maintenance Requirements | High (corrosion risk) | Low (polymer degradation-resistant) |
2. Silicone Rubber Heating Elements for Extreme Conditions
For applications requiring flexible, high-temperature-resistant heating cables, silicone rubber heating compounds are increasingly preferred. These materials withstand temperatures up to 200°C+, making them ideal for refinery heat tracing or offshore oil rigs. Their chemical-resistant properties also prevent degradation from H2S, acids, and alkalis—common challenges in hazardous industrial heating systems.
3. Fluoropolymer-Based Insulation for Corrosion Resistance
In marine and chemical plant environments, fluoropolymer-coated heating cables (e.g., FEP, PFA) provide superior moisture and chemical resistance compared to standard polyolefin heating cable jackets. This ensures long-term reliability in Zone 1 and Zone 2 explosive atmospheres.
Why Choose Advanced Polymer Compounds Over Metal Sheathed Cables?
While mineral-insulated (MI) heating cables have been the traditional choice for high-temperature industrial applications, polymer-based alternatives offer:
Lower installation costs (no need for explosion-proof conduit in some cases)
Faster thermal response due to better heat transfer in self-regulating heating systems
Easier maintenance (no risk of sheath corrosion, unlike stainless steel MI cables)
Emerging Trends: Smart Heating Cables with IoT Monitoring
The latest explosion-proof heating solutions integrate IoT-enabled temperature sensors within the conductive polymer matrix, allowing real-time monitoring via industrial automation systems (e.g., PLC, SCADA). This is particularly valuable in remote oil & gas facilities, where predictive maintenance can prevent costly downtime.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский











