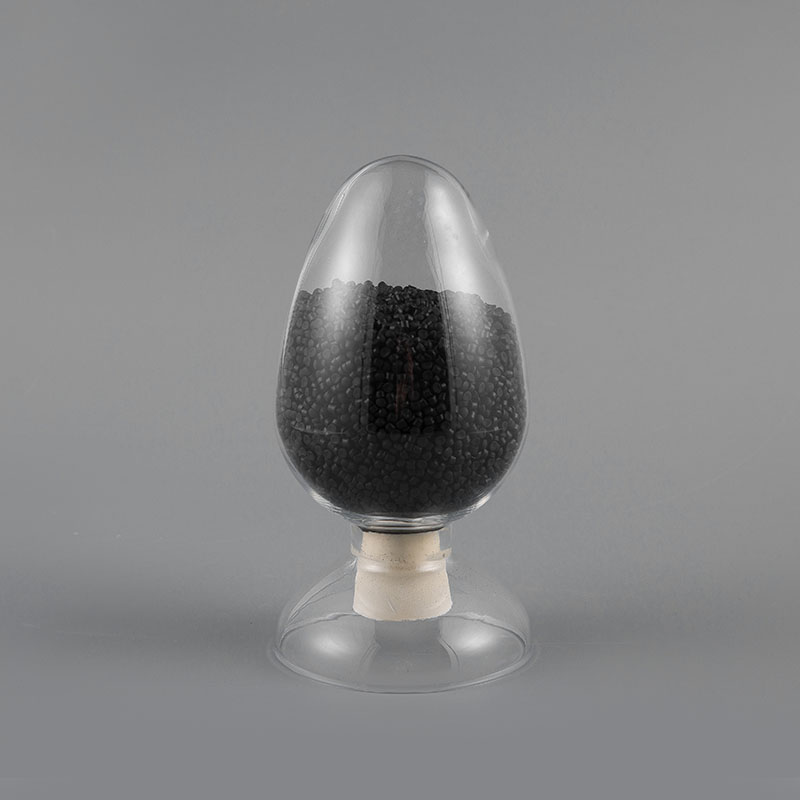
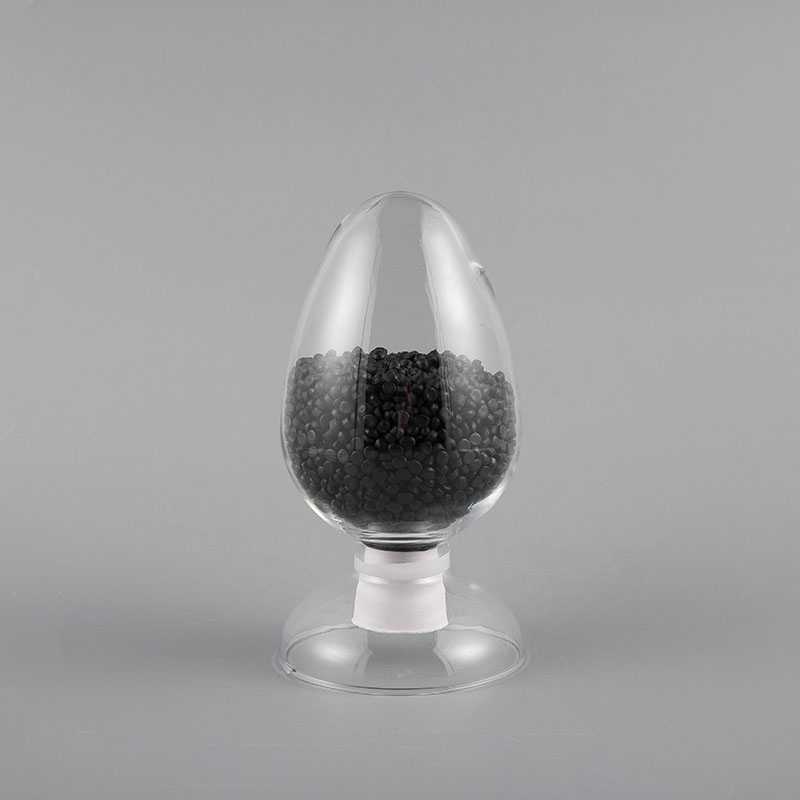
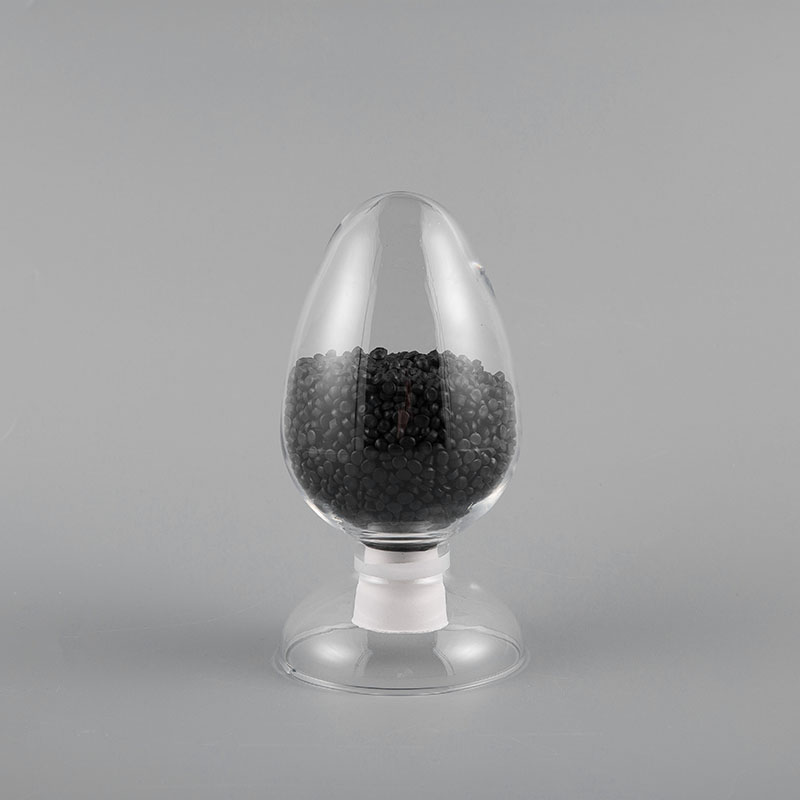
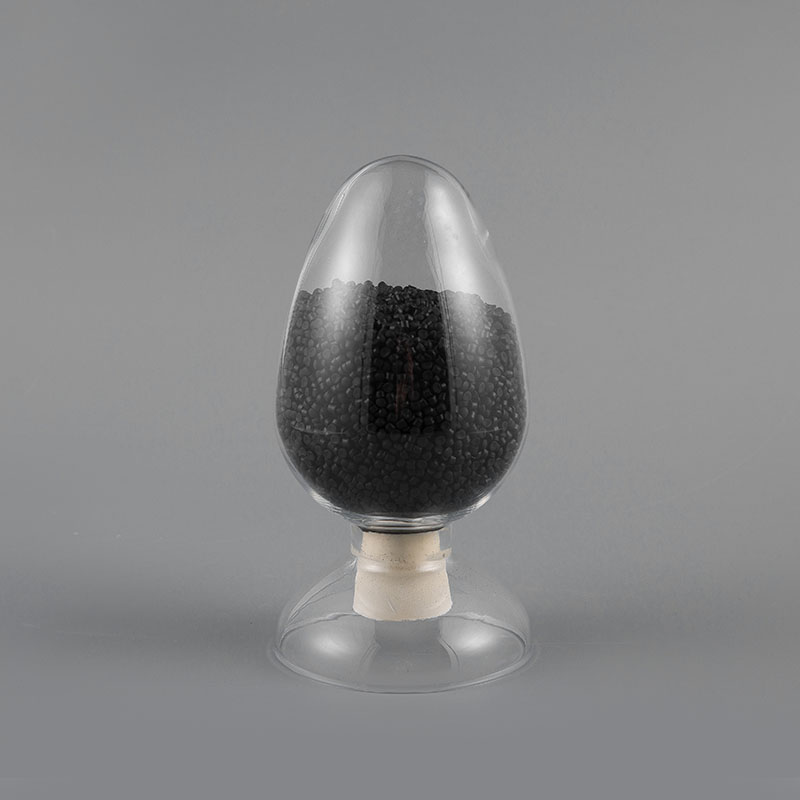
ZH-90 90℃ PVC Flame Retardant Soft Sheath Plastic has flame retardant properties and high temperatur...
ABOUT US
30YEARS OF
EXPERIENCE
About Us
Coming From China, Marketing To The World.
Hangzhou Meilin New Material Technology Co., Ltd. is China ODM/OEM Control Cable Compound Suppliers and Wholesale Control Cable Compound, we were established in July 1994 (formerly known as Zhejiang Lin'an Hongyan Plastic Factory). The company has two factories located at 619 Linglongshan Road and 259 Xingyu Street, Lingqiu Street, Linglong Industrial Park, Lin'an District, Hangzhou City. The registered capital of the company is 75 million yuan, covering an area of over 18000 square meters and a building area of over 30000 square meters. Currently, modern industrial factories and 18 advanced automated production lines have been built. The new factory area will be produced in 2021, making it the cleanest and most beautiful professional cable material manufacturer in the entire region—agreement conditions.
-
admin 12 Feb 2026
Why Are LSZH Compounds for Communication Cables Essentia...
Read MoreAs global data consumption surges, the architectural density of data centers and the complexity of public infrastructure have reached unprecedented levels. In these confined, high-value environments, ...
-
admin 04 Feb 2026
Meeting Global Compliance: Critical Requirements for PVC...
Read MoreThe global cable manufacturing landscape is undergoing a rigorous transition driven by stringent safety and environmental regulations. For industry professionals, understanding the technical nuances o...
-
admin 29 Jan 2026
Why Should You Switch to LSZH Compounds For Communicatio...
Read MoreIn the engineering of modern public infrastructure—such as subway systems, airports, and high-rise data centers—the selection of cabling materials is a critical safety decision. The transition from tr...
-
admin 22 Jan 2026
Navigating High-Speed Extrusion Challenges for LSZH Comp...
Read MoreAs global telecommunications infrastructure shifts toward 5G and high-density data centers, the demand for LSZH Compounds For Communication Cables has reached unprecedented levels. Unlike traditional ...
Control Cable Compound Industry Knowledge
Performance requirements and selection guide for composite materials for control cables
1. Composite materials for control cables
Control cables are widely used in industrial automation, power systems, rail transit and other fields. Their core function is to transmit signals or low-power electrical energy. The outer sheath and insulation layer of the cable usually adopt polymer composite materials, such as PVC (polyvinyl chloride), XLPE (cross-linked polyethylene), TPE (thermoplastic elastomer), etc. Different application scenarios have different requirements for material performance.
2. Key performance requirements
Electrical performance
Insulation resistance: To prevent current leakage, it must comply with standards such as IEC 60227/60245.
Dielectric strength: The ability to withstand high voltage breakdown, especially suitable for high-voltage environments.
Mechanical properties
Tensile strength and wear resistance: Ensure that the cable is not easily damaged during installation and dragging.
Flexibility: Frequent bending scenarios (such as robots and drag chain cables) require highly elastic materials (such as TPU).
Environmental adaptability
Temperature range:
PVC: -20°C~70°C
XLPE: -40°C~90°C
-Silicone rubber: -60°C~200°C (high temperature occasions).
Oil/chemical corrosion resistance: petrochemical, mining and other scenes require special formulas (such as CR chloroprene rubber).
Flame retardant and safety performance
Flame retardant grade: UL94 V-0, IEC 60332-1 (single vertical burning) or IEC 60332-3 (bundled burning).
Low halogen smoke (LSZH): low toxic smoke is required during combustion in confined spaces such as subways and tunnels.
Long-term reliability
Anti-aging: UV stabilizers are used for outdoor cables (such as photovoltaic power stations).
Hydrolysis stability: avoid material degradation in humid environments.
3. Selection Guide
Choose materials according to application scenarios
| Application Scenario | Recommended Material | Key Properties | Applicable Standards |
|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial Automation (Robotics, Drag Chains) | PVC / TPE / TPU | High flexibility, abrasion resistance, bend endurance | IEC 60228, UL 758 |
| High-Temperature Environments (Steel Plants, Boilers) | XLPE / Silicone Rubber | Heat resistance (-40°C~200°C), oxidation resistance | IEC 60502, UL 44 |
| Rail Transit (Subways, High-Speed Rail) | Halogen-Free Flame Retardant (LSZH) | Low smoke, non-toxic, flame retardant | EN 45545-2, BS 6853 |
| Marine Engineering (Ships, Offshore Platforms) | Saltwater-Resistant TPU / CR | Corrosion-proof, hydrolysis resistance, UV resistance | IEC 60092, IEEE 45 |
| Renewable Energy (Solar, Wind Power) | Cross-Linked Polyolefin (XLPO) | Weather resistance, UV protection | IEC 62930, UL 4703 |
| Petrochemical (Hazardous Areas) | Fluoroelastomer (FKM) | Oil/chemical resistance, flame retardant | API RP 14F, IEC 60079 |
Cost and performance balance
Economical: PVC (general scenario, lowest cost).
High performance: XLPE or TPU (long life, harsh environment).
Certification and standards
International standards: UL (US), CE (EU), RoHS (environmental protection).
Industry standards: GB/T (China), EN (Europe), IEEE (electricity).
4. Common problems and solutions
Question 1: Cable sheath cracking?
→ Check the cold resistance of the material (such as switching to XLPE) or whether the installation bending radius is too small.
Question 2: Severe signal interference?
→ Choose a composite structure with a shielding layer (such as aluminum foil + tinned copper wire).

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский











