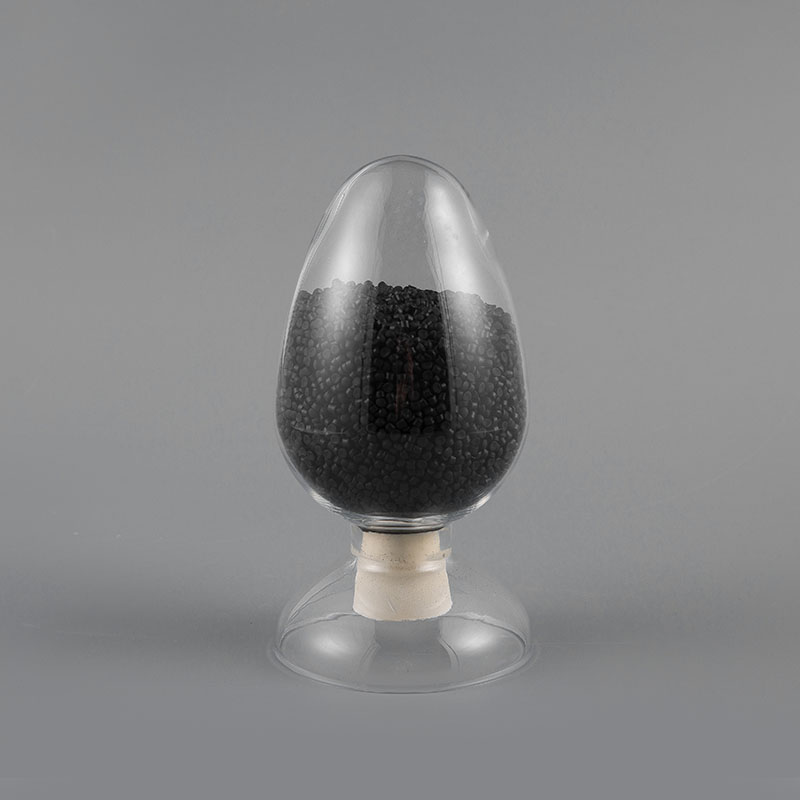
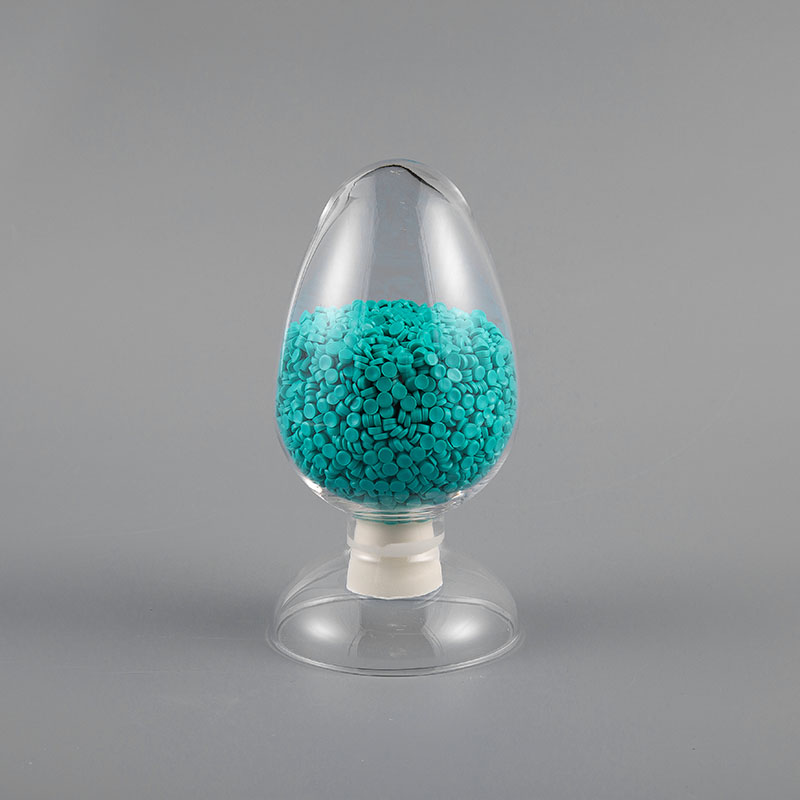
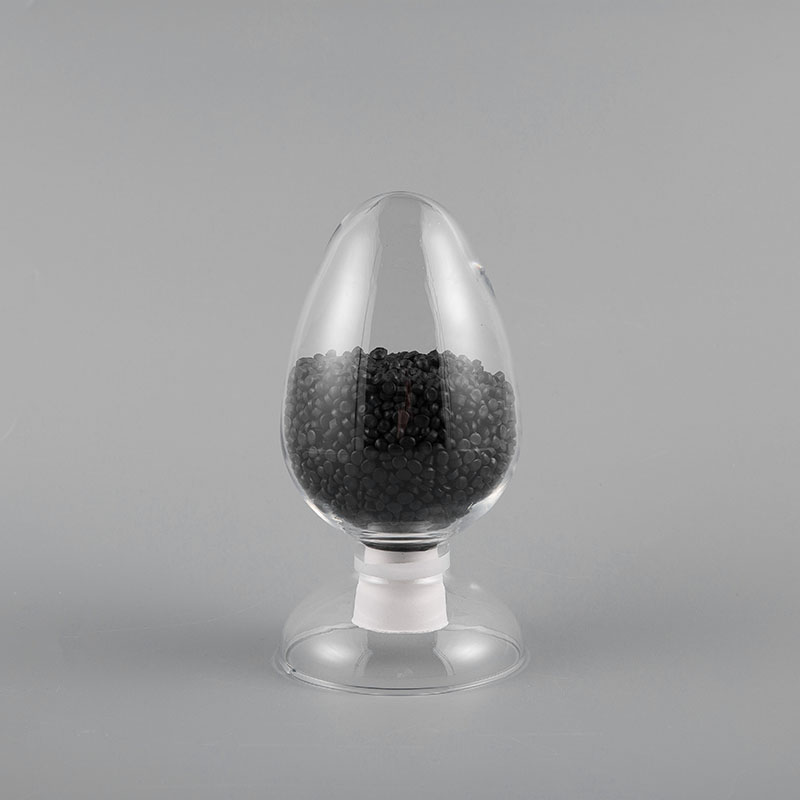
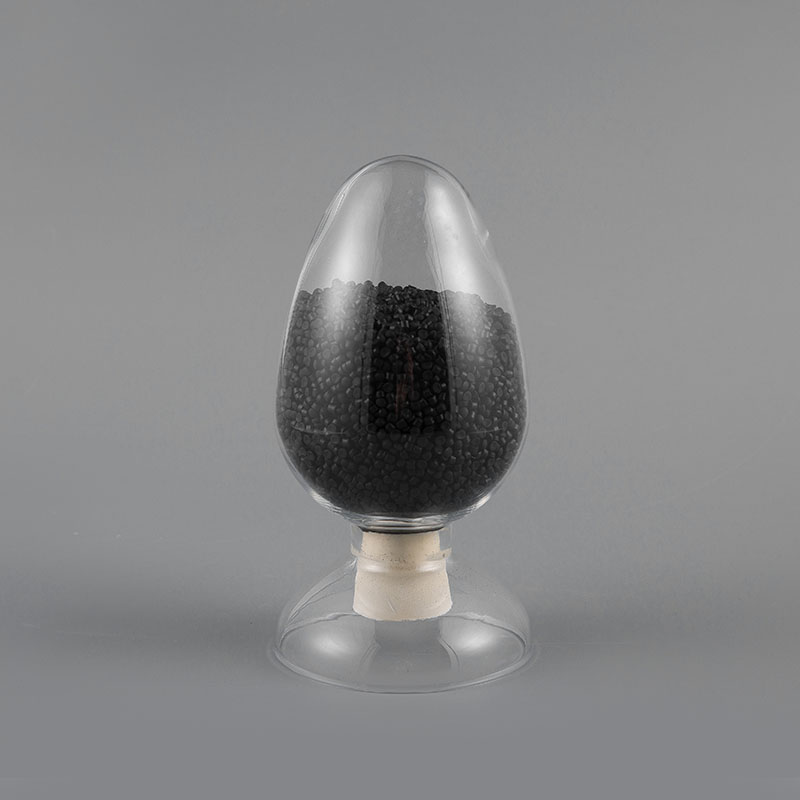
ULH-75 CMR 75℃ UL Standard CMR Grade Flame Retardant Network Cable Sheath Compound is a high-perform...
ABOUT US
30YEARS OF
EXPERIENCE
About Us
Coming From China, Marketing To The World.
Hangzhou Meilin New Material Technology Co., Ltd. is China ODM/OEM High Flame Retardant Network Cable/Coaxial Cable Compound Suppliers and Wholesale High Flame Retardant Network Cable/Coaxial Cable Compound, we were established in July 1994 (formerly known as Zhejiang Lin'an Hongyan Plastic Factory). The company has two factories located at 619 Linglongshan Road and 259 Xingyu Street, Lingqiu Street, Linglong Industrial Park, Lin'an District, Hangzhou City. The registered capital of the company is 75 million yuan, covering an area of over 18000 square meters and a building area of over 30000 square meters. Currently, modern industrial factories and 18 advanced automated production lines have been built. The new factory area will be produced in 2021, making it the cleanest and most beautiful professional cable material manufacturer in the entire region—agreement conditions.
-
admin 12 Feb 2026
Why Are LSZH Compounds for Communication Cables Essentia...
Read MoreAs global data consumption surges, the architectural density of data centers and the complexity of public infrastructure have reached unprecedented levels. In these confined, high-value environments, ...
-
admin 04 Feb 2026
Meeting Global Compliance: Critical Requirements for PVC...
Read MoreThe global cable manufacturing landscape is undergoing a rigorous transition driven by stringent safety and environmental regulations. For industry professionals, understanding the technical nuances o...
-
admin 29 Jan 2026
Why Should You Switch to LSZH Compounds For Communicatio...
Read MoreIn the engineering of modern public infrastructure—such as subway systems, airports, and high-rise data centers—the selection of cabling materials is a critical safety decision. The transition from tr...
-
admin 22 Jan 2026
Navigating High-Speed Extrusion Challenges for LSZH Comp...
Read MoreAs global telecommunications infrastructure shifts toward 5G and high-density data centers, the demand for LSZH Compounds For Communication Cables has reached unprecedented levels. Unlike traditional ...
High Flame Retardant Network Cable/Coaxial Cable Compound Industry Knowledge
Application scenarios of high flame retardant cable composites: fire safety requirements from data centers to rail transit
High flame retardant cable composites are crucial in areas with strict fire safety requirements. Their core applications include data centers, smart buildings, rail transit, energy and power, and industrial automation. Different scenarios have differentiated requirements for cable flame retardancy, low smoke zero halogen (LSZH), high temperature resistance and other properties.
1. Data center: fire protection under high-density wiring
Core requirements:
High flame retardancy (IEC 60332-3A / UL 94 V-0): prevent fire from spreading in dense cables.
Low smoke zero halogen (LSZH): reduce toxic smoke, ensure personnel escape and equipment safety.
High temperature resistance (90°C~125°C): adapt to high-load heat dissipation environment of servers.
Typical materials:
Halogen-free flame retardant polyolefins (FR-PE/FR-PP), such as Dow Chemical's ECCOH™.
Ceramic silicone rubber (forms a fire barrier at extreme high temperatures).
Industry standards:
TIA-942 (data center cabling standard) requires cables to pass IEC 60332-3A and UL 910 (Plenum level).
2. Rail transit: high safety requirements for carriages and tunnels
Core requirements:
Low smoke and non-toxic (EN 45545-2): EU standards strictly control the release of combustion toxic gases (such as CO, HCL).
Oil resistant and vibration resistant: adapt to the locomotive operating environment.
Bundled flame retardant (IEC 60332-3C and above): prevent the spread of fire in the tunnel.
Typical materials:
Halogen-free cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE): has both flame retardancy and mechanical strength.
Flame retardant PVC (containing phosphorus flame retardant): low cost, but must comply with RoHS.
Industry standards:
EN 45545-2 (EU railway fire protection), GB/T 19666 (China flame retardant cable standard).
3. Smart Buildings: Fire Safety in Building Automation
Core Requirements:
CMR (UL 1666): Vertical shaft cables must prevent fire from spreading across floors.
Low Smoke (IEC 61034): Reduce the risk of people inhaling toxic smoke.
Flexible Design: Facilitates complex wiring.
Typical Materials:
Flame-retardant PVC (containing Sb₂O₃ synergist): Widely used in ordinary building cables.
LSZH Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE): Replaces PVC for high-end projects.
Industry Cases:
NFPA 70 (NEC) in the United States requires CMR/MPR-grade cables for high-rise buildings.
4. Energy and Power: Long-term Reliability in Harsh Environments
Core Requirements:
High Temperature Resistance (150°C+): For example, photovoltaic cables must withstand UV and high temperatures.
Oil/Chemical Resistance: Petrochemical Plants, Offshore Wind Power Scenarios.
High Flame Retardant (IEC 60332-3B): Prevent fires in substations.
Typical materials:
Cross-linked halogen-free polyolefin (XLPO): used for photovoltaic cables (such as TUV certification).
Fluoroplastic (such as PTFE): high-cost solution in extreme environments.
Industry standards:
IEC 62930 (photovoltaic cables), IEEE 383 (nuclear power plant cables).
5. Industrial automation: safety protection of equipment and production lines
Core needs:
Anti-mechanical damage: friction and extrusion protection in factory environments.
Flame retardant + oil resistant (UL 1277): such as robot cables.
EMI shielding: prevent signal interference (coaxial cable applications).
Typical materials:
Flame retardant polyurethane (PUR): excellent wear resistance, suitable for drag chain cables.
Shielding materials containing aluminum and magnesium layers: improve anti-interference capabilities.
Selection logic of high flame retardant cable composite materials
| Application Scenario | Core Requirements | Recommended Material | Key Standards |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Center | High flame retardancy, low smoke | Halogen-free polyolefin | IEC 60332-3A, UL 910 |
| Rail Transportation | Low toxicity, vibration resistance | XLPE / LSZH | EN 45545-2, GB/T 19666 |
| Smart Building | Shaft fireproofing, flexibility | PVC / LSZH-TPE | UL 1666, IEC 61034 |
| Energy & Power | High temp. resistance, weatherproof | XLPO / PTFE | IEC 62930, IEEE 383 |
| Industrial Automation | Abrasion resistance + flame retardancy | PUR / Shielded material | UL 1277, IEC 61158 |

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский













