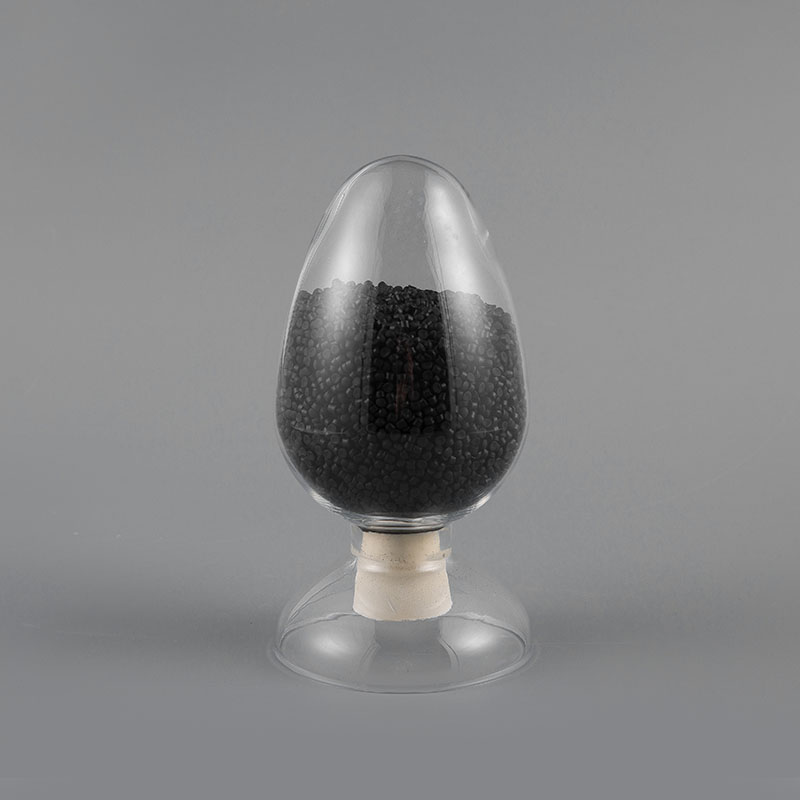
AVSS 80℃ Automotive Thin-Wall Low Voltage Wire Compound is a wire material specially designed for th...
ABOUT US
30YEARS OF
EXPERIENCE
About Us
Coming From China, Marketing To The World.
Hangzhou Meilin New Material Technology Co., Ltd. is China ODM/OEM Low-Voltage Automotive Cable Compound Suppliers and Wholesale Low-Voltage Automotive Cable Compound, we were established in July 1994 (formerly known as Zhejiang Lin'an Hongyan Plastic Factory). The company has two factories located at 619 Linglongshan Road and 259 Xingyu Street, Lingqiu Street, Linglong Industrial Park, Lin'an District, Hangzhou City. The registered capital of the company is 75 million yuan, covering an area of over 18000 square meters and a building area of over 30000 square meters. Currently, modern industrial factories and 18 advanced automated production lines have been built. The new factory area will be produced in 2021, making it the cleanest and most beautiful professional cable material manufacturer in the entire region—agreement conditions.
-
admin 12 Feb 2026
Why Are LSZH Compounds for Communication Cables Essentia...
Read MoreAs global data consumption surges, the architectural density of data centers and the complexity of public infrastructure have reached unprecedented levels. In these confined, high-value environments, ...
-
admin 04 Feb 2026
Meeting Global Compliance: Critical Requirements for PVC...
Read MoreThe global cable manufacturing landscape is undergoing a rigorous transition driven by stringent safety and environmental regulations. For industry professionals, understanding the technical nuances o...
-
admin 29 Jan 2026
Why Should You Switch to LSZH Compounds For Communicatio...
Read MoreIn the engineering of modern public infrastructure—such as subway systems, airports, and high-rise data centers—the selection of cabling materials is a critical safety decision. The transition from tr...
-
admin 22 Jan 2026
Navigating High-Speed Extrusion Challenges for LSZH Comp...
Read MoreAs global telecommunications infrastructure shifts toward 5G and high-density data centers, the demand for LSZH Compounds For Communication Cables has reached unprecedented levels. Unlike traditional ...
Low-Voltage Automotive Cable Compound Industry Knowledge
Compared with ordinary cable masterbatches, what are the special requirements and advantages of low-voltage automotive cable masterbatches in terms of temperature resistance?
Compared with ordinary cable masterbatches, low-voltage automotive cable masterbatches have the following special requirements and advantages in terms of temperature resistance:
Special requirements
Wide operating temperature range: The working environment of the car is complex and changeable, and the temperature of parts such as the engine compartment is high, while the external cables of the vehicle in cold areas will face low temperature environments. Therefore, low-voltage automotive cable masterbatches usually need to meet a wider operating temperature range, and are generally required to be able to work stably for a long time at -40℃ to 125℃ or even higher temperatures to ensure that the cable can be used normally under various climatic conditions and vehicle operating conditions.
Short-term high temperature shock resistance: During the operation of the car, short-term high temperature shocks may occur, such as local high temperatures caused by the engine starting moment or certain electrical equipment failures. Low-voltage automotive cable masterbatches need to have good short-term high temperature shock resistance, and can withstand 150℃ or even higher temperatures in a short period of time without significant performance degradation, deformation or damage, so as to ensure the safety and reliability of the cable.
Good temperature and aging resistance: The service life of cars is usually long, and cables will be continuously affected by temperature during long-term use. Masterbatches for low-voltage automotive cables need to have excellent temperature and aging resistance. After a long period of high temperature, they can still maintain the stability of their physical, electrical and mechanical properties, reduce the risk of cable failure due to aging, and meet the requirements of the entire service life cycle of the car.
Advantages
Using high-performance materials: Masterbatches for low-voltage automotive cables usually use high-performance polymer materials, such as special polyolefins, fluoroplastics, etc. These materials themselves have high heat resistance and thermal stability. Compared with the materials commonly used in ordinary cable masterbatches, they can maintain good mechanical properties and insulation properties at higher temperatures. For example, fluoroplastics have excellent high temperature resistance and can be used for a long time above 200°C.
Adding special heat-resistant additives: In order to further improve the temperature resistance, various special heat-resistant additives such as antioxidants and heat stabilizers are added to masterbatches for low-voltage automotive cables. These additives can inhibit the oxidative degradation reaction of polymers at high temperatures, improve the thermal stability of masterbatches, and enable them to maintain good performance in high temperature environments. Compared with ordinary cable masterbatches, the types and amounts of additives added are more precisely formulated to meet the special temperature resistance requirements of automotive cables.
Optimized processing technology: During the production process, low-voltage automotive cable masterbatches use optimized processing technology, such as precise control of extrusion temperature, pressure and cooling rate parameters, so that the masterbatch has a more uniform microstructure and better crystallinity, thereby improving its temperature resistance. Compared with the processing technology of ordinary cable masterbatches, more attention is paid to details and precision control to ensure that each batch of products can achieve stable temperature resistance performance indicators.
What key ingredients are usually included in the formula of low-voltage automotive cable masterbatches to improve the mechanical strength and flexibility of the cable to adapt to the complex use environment of the car?
The formula of low-voltage automotive cable masterbatches usually contains the following key ingredients to improve the mechanical strength and flexibility of the cable:
Base polymer: It is the main component of the masterbatch, such as high-performance polyolefins, ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA), thermoplastic elastomer (TPE), etc. High-performance polyolefins have good mechanical strength and chemical resistance; EVA has good flexibility and low-temperature performance, and can maintain the softness of cables in low-temperature environments; TPE has both the elasticity of rubber and the processing performance of plastics, which can significantly improve the flexibility and fatigue resistance of cables.
Plasticizers: commonly used are phthalates, fatty acid esters, etc. Plasticizers can be inserted between polymer molecular chains, weaken the forces between molecular chains, and make molecular chains easier to move, thereby increasing the flexibility and plasticity of cables. At the same time, it can also improve the processing performance of masterbatches and reduce processing temperature and pressure.
Reinforcement fillers: such as calcium carbonate, talcum powder, glass fiber, etc. These fillers can improve the mechanical strength, hardness and wear resistance of cables. Calcium carbonate is inexpensive and can increase the volume of masterbatches, reduce costs, and increase certain strength; talcum powder can improve the processing performance and mechanical properties of masterbatches, and improve the heat resistance and dimensional stability of cables; glass fiber can significantly improve the tensile strength and rigidity of cables, but excessive addition may affect the flexibility of cables and needs to be reasonably controlled.
Antioxidants: In order to prevent the polymer from being degraded due to oxidation during processing and use, which affects the performance of the cable, antioxidants such as hindered phenols and phosphites are usually added. Antioxidants can capture free radicals, prevent oxidation reactions, extend the service life of the cable, and maintain the stability of its mechanical strength and flexibility.
Lubricants: Including fatty acids and their esters, paraffin, etc. Lubricants can reduce the friction between polymer molecular chains and between polymers and processing equipment, improve the processing fluidity of masterbatches, make the cable surface smoother, and also help improve the flexibility of the cable and reduce damage to the internal structure during bending.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский












