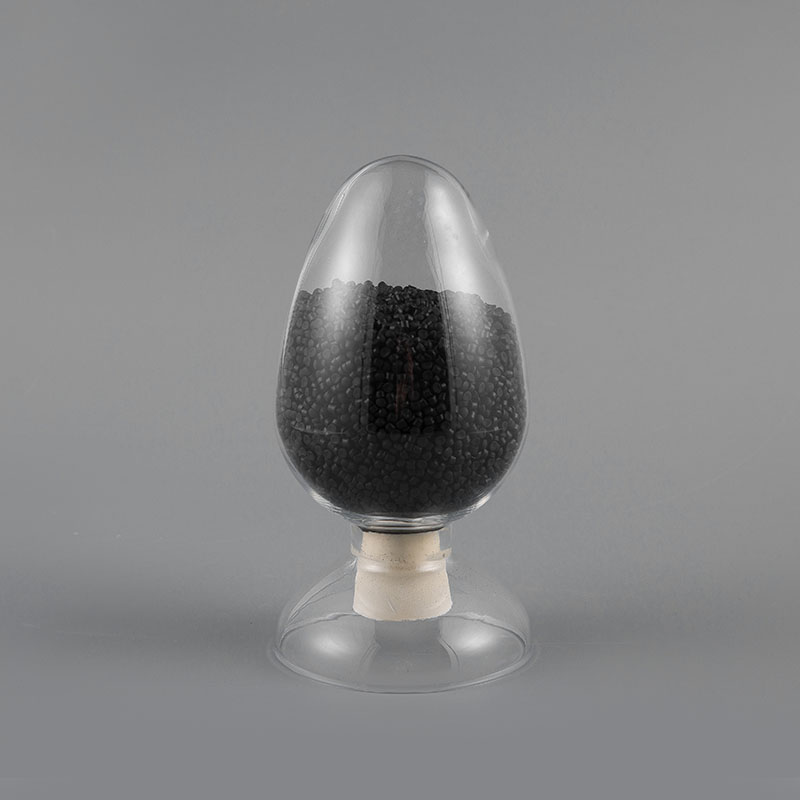
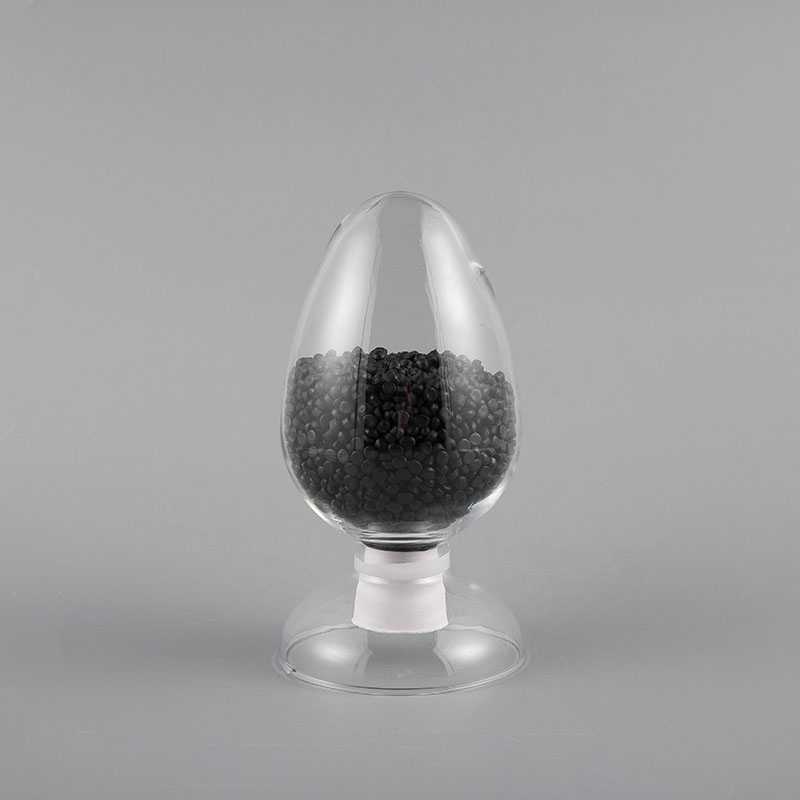
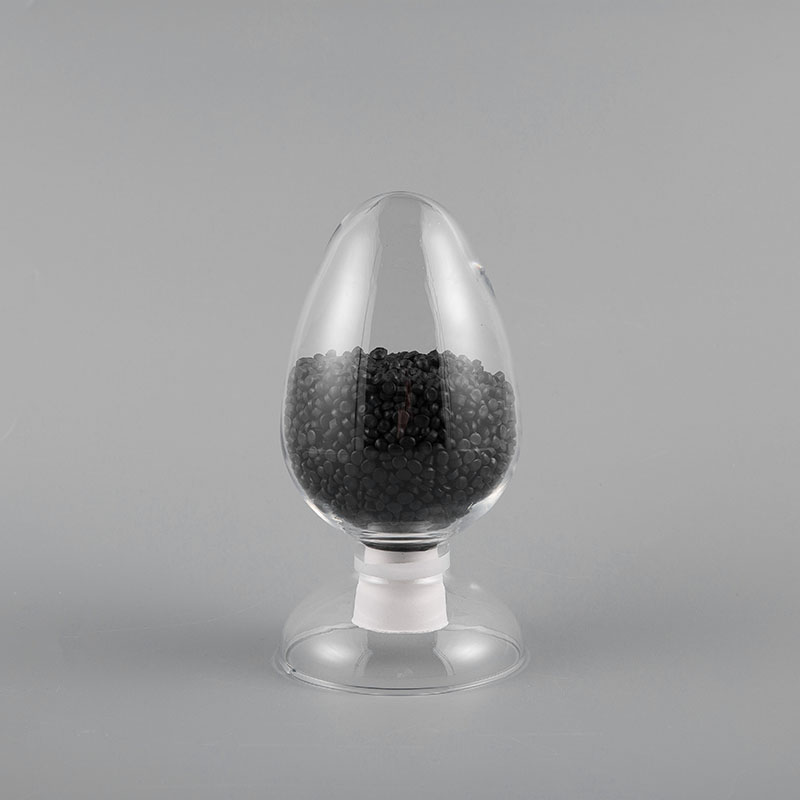
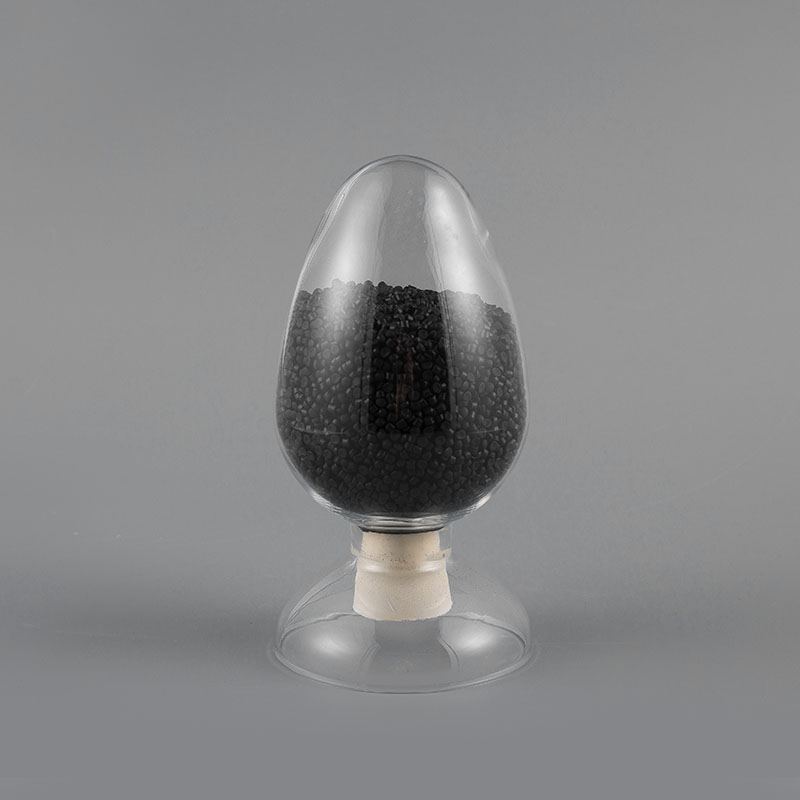
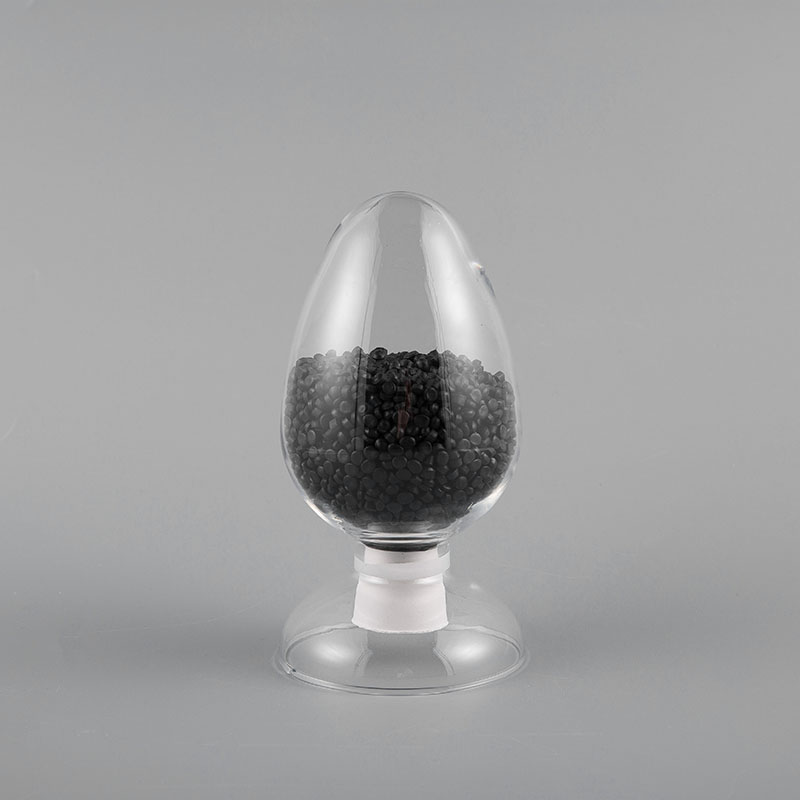
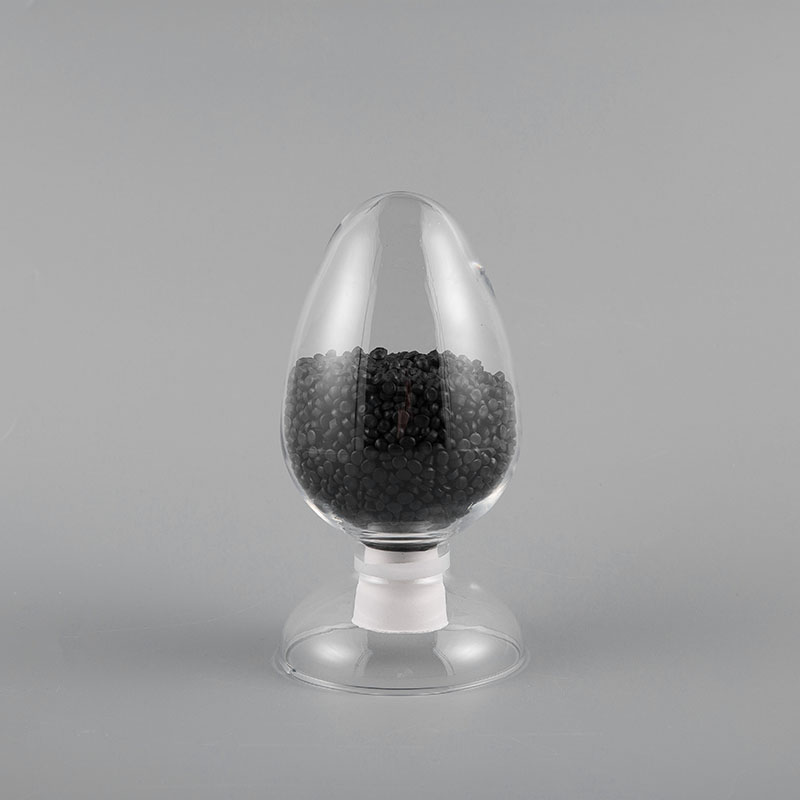
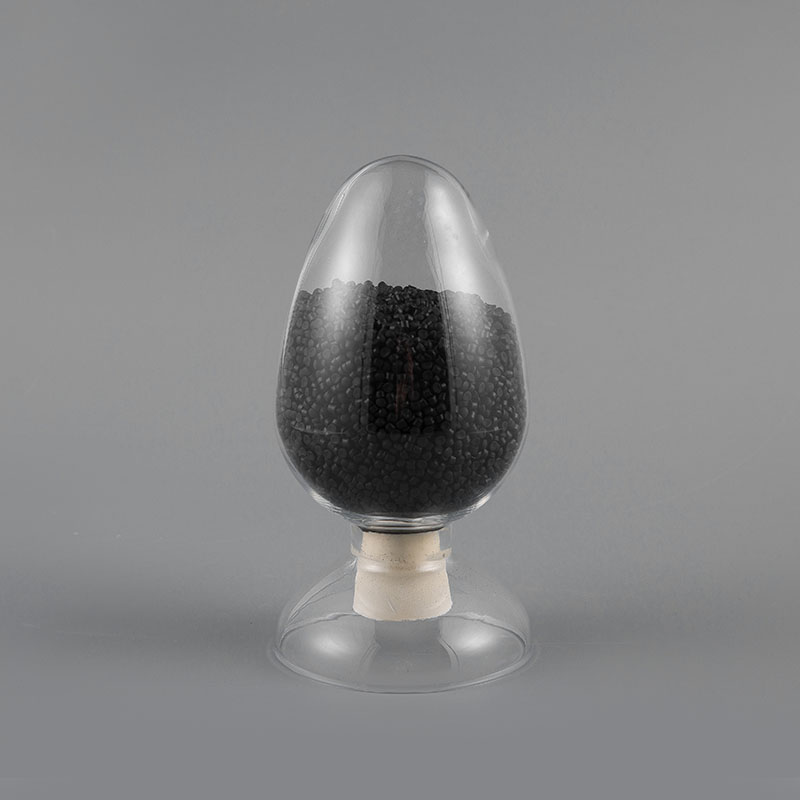
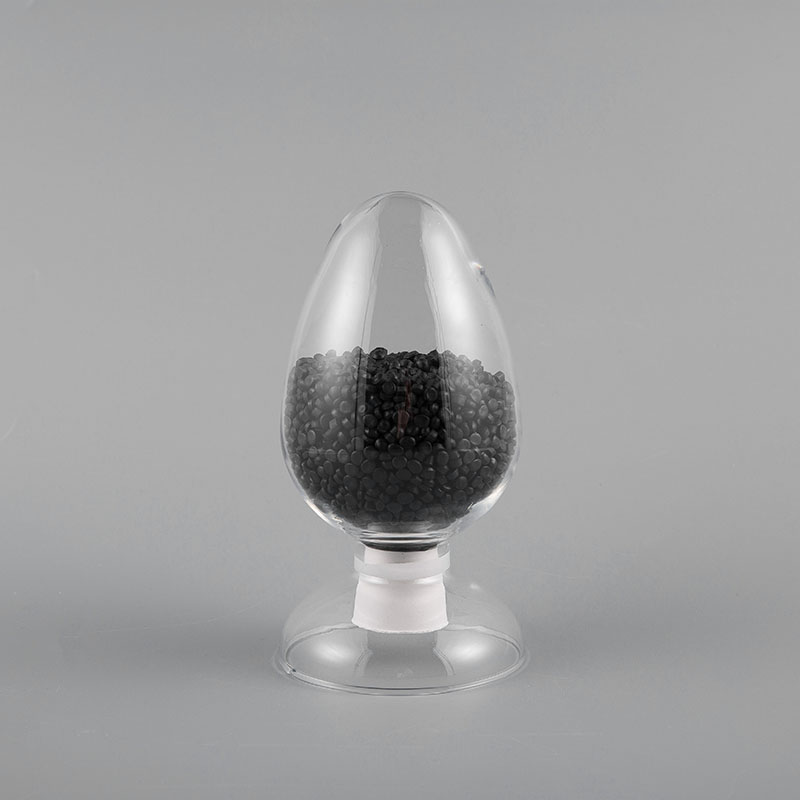
ZH-70 70℃ PVC Flame Retardant Soft Sheath Plastic has flame retardant properties and softness. It ma...
ABOUT US
30YEARS OF
EXPERIENCE
About Us
Coming From China, Marketing To The World.
Hangzhou Meilin New Material Technology Co., Ltd. is China ODM/OEM Medium/Low Voltage Heating Cable Compound Suppliers and Wholesale Medium/Low Voltage Heating Cable Compound, we were established in July 1994 (formerly known as Zhejiang Lin'an Hongyan Plastic Factory). The company has two factories located at 619 Linglongshan Road and 259 Xingyu Street, Lingqiu Street, Linglong Industrial Park, Lin'an District, Hangzhou City. The registered capital of the company is 75 million yuan, covering an area of over 18000 square meters and a building area of over 30000 square meters. Currently, modern industrial factories and 18 advanced automated production lines have been built. The new factory area will be produced in 2021, making it the cleanest and most beautiful professional cable material manufacturer in the entire region—agreement conditions.
-
admin 12 Feb 2026
Why Are LSZH Compounds for Communication Cables Essentia...
Read MoreAs global data consumption surges, the architectural density of data centers and the complexity of public infrastructure have reached unprecedented levels. In these confined, high-value environments, ...
-
admin 04 Feb 2026
Meeting Global Compliance: Critical Requirements for PVC...
Read MoreThe global cable manufacturing landscape is undergoing a rigorous transition driven by stringent safety and environmental regulations. For industry professionals, understanding the technical nuances o...
-
admin 29 Jan 2026
Why Should You Switch to LSZH Compounds For Communicatio...
Read MoreIn the engineering of modern public infrastructure—such as subway systems, airports, and high-rise data centers—the selection of cabling materials is a critical safety decision. The transition from tr...
-
admin 22 Jan 2026
Navigating High-Speed Extrusion Challenges for LSZH Comp...
Read MoreAs global telecommunications infrastructure shifts toward 5G and high-density data centers, the demand for LSZH Compounds For Communication Cables has reached unprecedented levels. Unlike traditional ...
Medium/Low Voltage Heating Cable Compound Industry Knowledge
What is the application of medium and low voltage heating cable composite materials in building heating systems?
The application of medium and low voltage heating cable composite materials in building heating systems is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
1. Floor heating (electric floor heating)
Medium and low voltage heating cables are widely used in floor heating systems of buildings, especially in cold areas. By laying heating cables under the ground or in the floor, the ground is heated by converting electrical energy into thermal energy, thereby providing a comfortable warm environment indoors. This floor heating system is usually composed of composite heating cables, which have excellent high temperature resistance and can withstand long-term high-load work, while effectively ensuring the uniformity and stability of heating.
2. Pipeline antifreeze
In cold climates, water pipes, drain pipes or other important pipes in buildings are prone to freezing, which may cause pipe rupture or leakage. Medium and low voltage heating cable composite materials can be wrapped or embedded in pipes to provide continuous heat to prevent water pipes from freezing. This system not only ensures the safety of the pipes, but also avoids maintenance costs and unnecessary losses caused by freezing.
3. Roof snow melting system
In winter, snow and ice may accumulate on roofs and eaves, especially on sloping roofs. Heating cable composites can be embedded in the roof or eaves, and the electric heating system can effectively melt snow and avoid roof damage caused by heavy snow or freezing. In addition, this system can effectively prevent the formation of ice cones and reduce potential threats to the exterior of the building.
4. Anti-slip system
Medium and low voltage heating cable composites can be used for anti-slip systems on the exterior of buildings, especially in places such as stairs, walkways, and driveways. In cold weather, these areas are prone to become very slippery due to snow and ice, increasing the risk of falling. By burying heating cables in these areas, snow can be automatically melted when it snows or freezes, keeping the ground dry and warm, thereby reducing the occurrence of slips and accidents.
5. Self-regulating function
Modern medium and low voltage heating cable composites usually have self-regulating functions, which means that they can automatically adjust the heating power according to changes in ambient temperature. For example, when the temperature is low, the heating cable will automatically increase the heating output to ensure the heating effect; when the ambient temperature rises, the system will automatically reduce the power to save energy and avoid overheating. This ensures that the heating system inside and outside the building is both efficient and energy-saving.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский


















